This post describes successive comparison type ADCs.
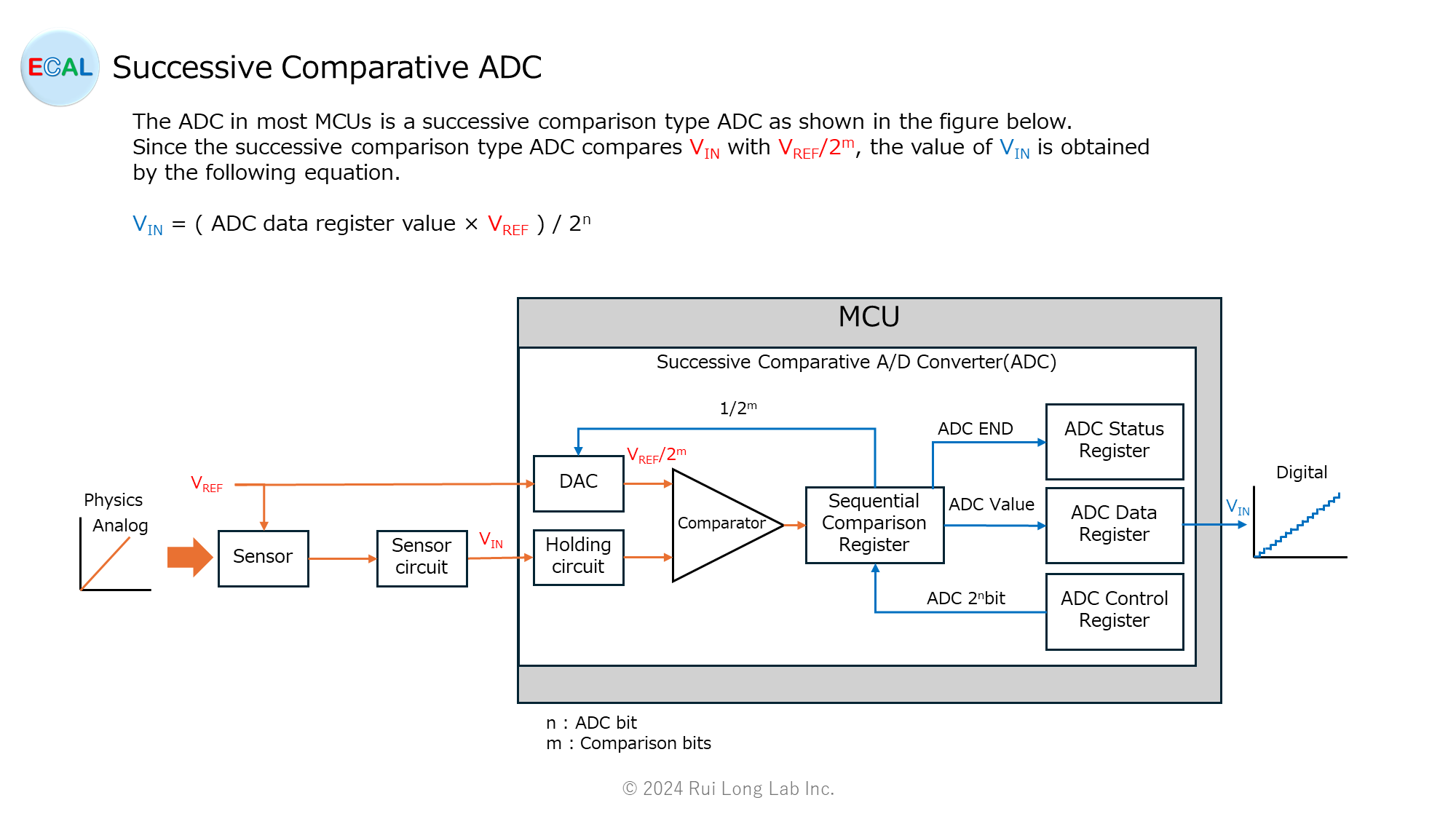
The ADC in most MCUs is a successive comparison type ADC as shown in the figure below. Since the successive comparison type ADC compares VIN with VREF/2m, the value of VIN is obtained by the following equation.
VIN = ( ADC data register value × VREF ) / 2n
Examples of ADC programs that take into account various issues
- Check if ADC is running
- ADC Start & Check
- Timeout when ADC is not completed within a predetermined time
ADC conversion time varies with ADC 2n bits, so timeout TIME_OUT_ADC is also adjusted. - ADC read
#define TIME_OUT_ADC 10 // 10[us]
// Sample HAL function
int hal_adc_status( int ); // ADC status read function
int hal_adc_start( int ); // ADC start function
int hal_adc_read( int ); // ADC read function
bool time_out( int ); // Time out function [us]
int ADC_Read( int ch)
{
bool flag = FALSE;
int val = 0;
// Check if ADC is running
if( hal_adc_status( ch ) == ADC_FIN )
{
// ADC start
if( hal_adc_start( ch ) == ADC_EXE )
{
flag = TRUE;
do{
// Check Time out
if( time_out( TIME_OUT_ADC ) == TRUE )
{
flag = FALSE;
break;
}
// Check ADC fin
}while( hal_adc_status( ch ) == ADC_FIN )
}
}
if( flag == TRUE )
{
// ADC read
val = hal_adc_read( ch );
}
return( val );
}Simple ADC program example
- ADC start and ADC conversion wait, ADC read
// Sample HAL function
int hal_adc_start_read( int ); // ADC start & read function
int ADC_Read( int ch)
{
// ADC start & read
return( hal_adc_start_read( ch ) );
}