This posting describes SMP (Symmetric Multi-Processing) and AMP (Asymmetric Multi-Processing).
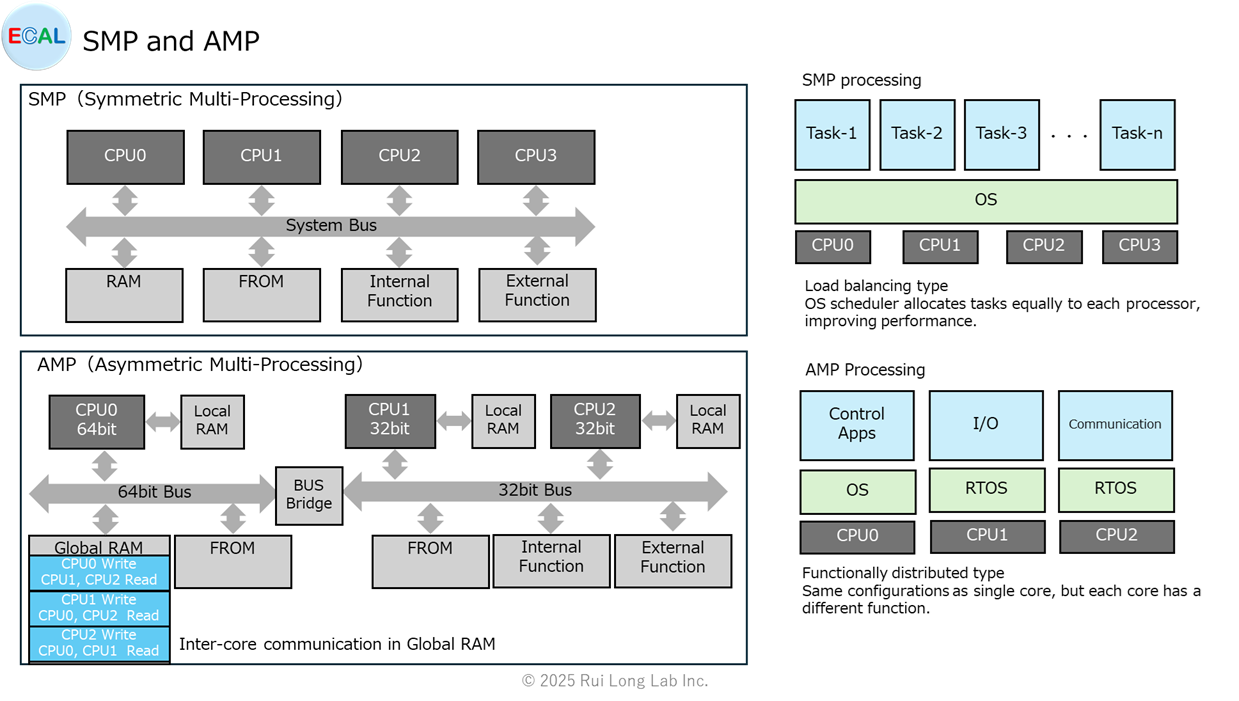
Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP)
Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP) is an architecture in which multiple processors (or cores) share the same memory space and process tasks symmetrically.Each processor operates independently but plays an equal role on the same operating system (OS).
Asymmetric Multi-Processing (AMP)
Asymmetric Multi-Processing (AMP) is a multi-processing architecture in which multiple processors or cores have asymmetric roles and operate specifically for a particular task.Unlike Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP), where tasks are processed equally among processors, AMP allows each processor to have a different function.
Comparison of SMP and AMP
| Item | SMP | AMP |
|---|---|---|
| Role of the Processor | All processors are equal and can handle the same tasks. | Different roles for each processor (master-slave structure). |
| Memory access | Use shared memory (single memory space). | Different memory configurations are possible per processor (shared or dedicated). |
| OS Management | Single OS manages all processors. | Different OS and firmware can be run on each processor. |
| Task Assignment | OS scheduler allocates tasks evenly. | Assign tasks uniquely to each processor. |
| Parallel processing | Parallel processing is possible on all processors. | Parallel processing is possible, but load balancing is less flexible. |
| Real time processing | Real-time performance is generally low (latency-prone). | Can be dedicated to specific processors for real-time processing. |
| Power efficiency | All processors operate at the same power level. | Low-power and high-performance processors can be used separately. |
| Implementation complexity | Relatively simple (managed by OS). | Requires advanced design (inter-processor communication and task allocation considerations). |
| Main applications | PC, servers, general purpose computing. | Embedded systems, mobile devices, real-time control. |
| Typical example | x86 multi-core CPUs (Intel, AMD), servers, workstations. | ARM big.LITTLE, embedded systems (automotive ECU, robot control). |
