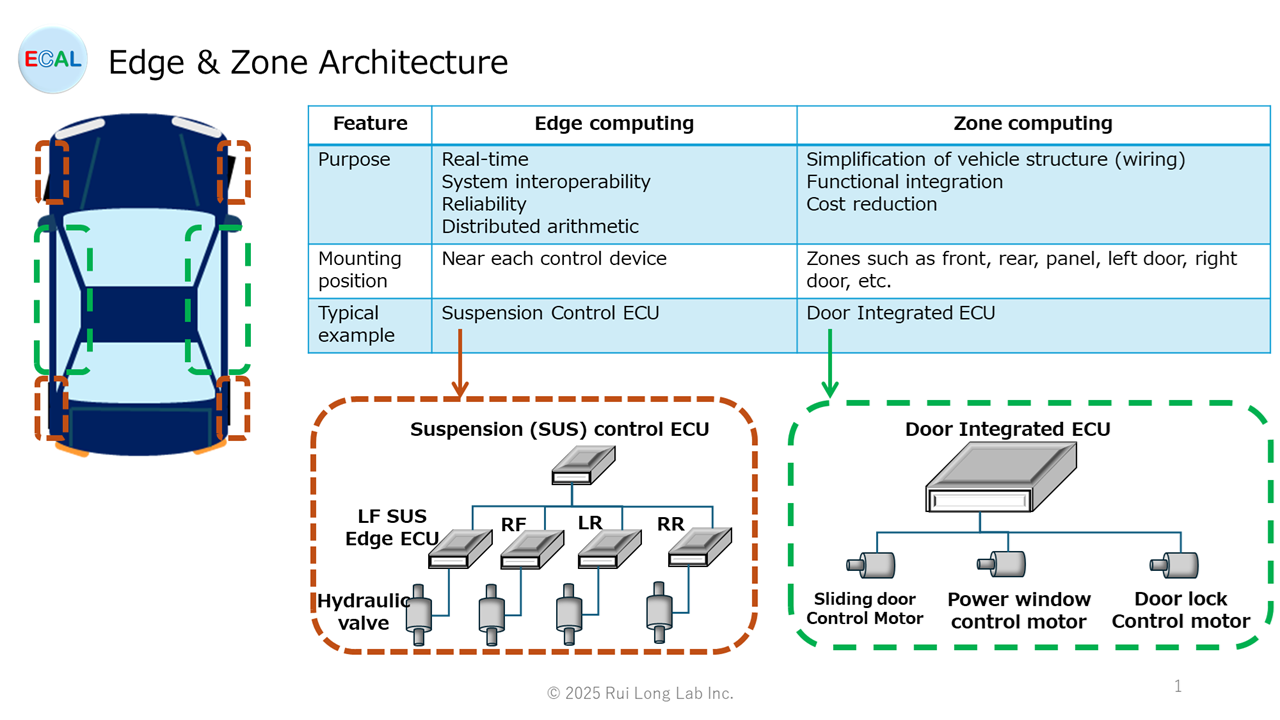
With the recent development of SDV (Software Defined Vehicle), which is a hot topic, ECU architecture is shifting from domain architecture to edge architecture, zone architecture, and combined edge & zone architecture. OSS-ECAL is an OSS suitable for porting sensors, actuators, external memory, and other components associated with architectural changes.
When sensors and actuators are moved between ECUs, portability of the corresponding software becomes a major issue. OSS-ECAL solves this issue and enables a smooth transition.
OSS-ECAL is a proprietary OSS that has nothing to do with AUTOSAR.
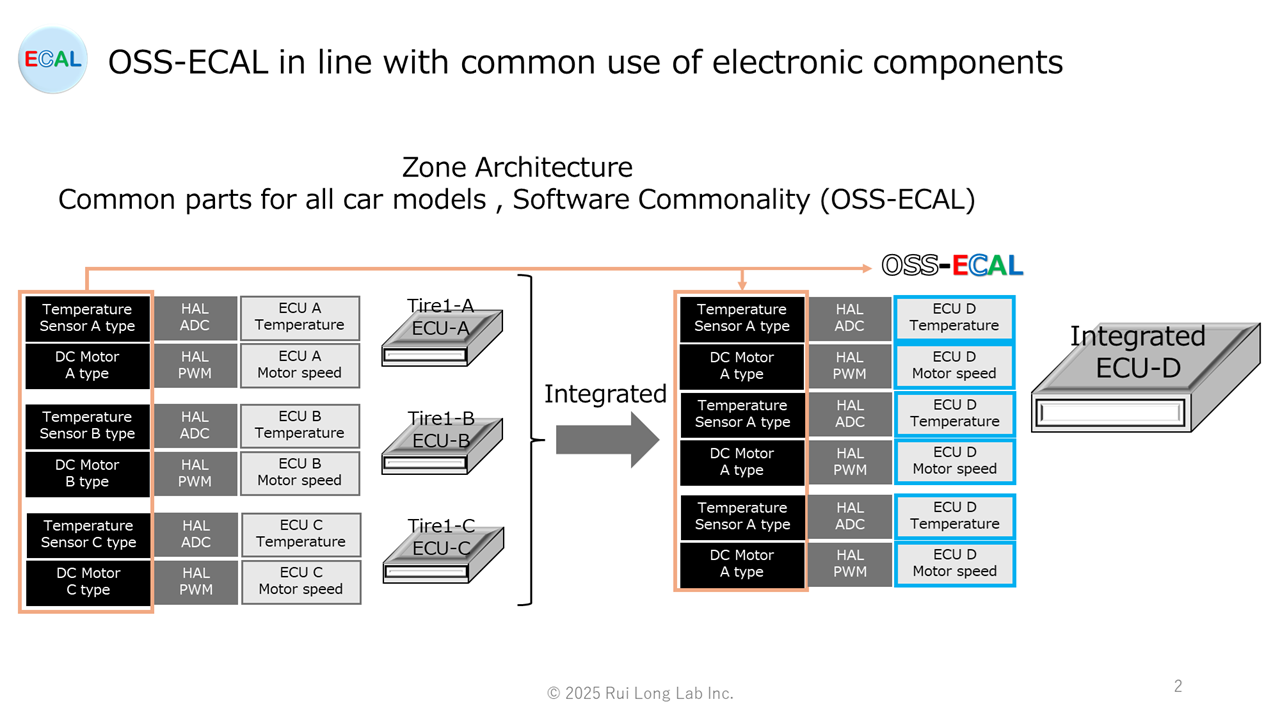
OSS-ECAL in line with common use of electronic components
With the shift to Edge and Zone architecture, we believe that cost reductions can be expected through centralized purchasing by standardizing the sensors and actuators used in each ECU and the external memory across all vehicle models.
However, if the software for sensors, actuators, and external memory is developed individually by each Tier 1 manufacturer, it will result in wasted time and cost.
Therefore, by using OSS-ECAL, software development time can be shortened, development costs can be reduced, and quality can be improved through common use.
SDV
Regarding SDV (Software Defined Vehicle), not only issues related to ECU rewriting, but also vehicle APIs, automated driving, ECU architecture, security, data centers, AI, CPUs for AI (GPUs, NPUs, SoCs), high-speed memory, etc. are mentioned.The following is a brief overview of the SDVs.This post is organized to include past posts on SDV.Please note that I am not an expert on SDV and there may be differences from actual SDV.
Development phase of SDV
SDVs would be divided into the following development phasesI am not sure about the vehicle API, so I have left it undocumented.
| Development Phase | Main Functions | Outline | Development |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 OTA function installed | Over The Air(OTA) | – ECU Re-Programming – Re-Programming Security | 1-1 OTA 1-2 Security Standard Proprietary standards 1-3 Next-generation in-vehicle equipment and ECU architecture definition 1-4 MBD Agile Development Environment |
| Phase 2 Enhanced telematics functionality | User’s Application | – Applications SNS, GAME, VOD, Payment, Generate AI, Concierge AI, Private Information Security | 2-1 User personal information security Usage history and Information concealment |
| Phase 3 Automated Driving and Ridesharing | Automated Driving | – Ridesharing – Payment – Automated Driving – Automatic parking | 3-1 Vehicle API 3-2 Automated AI 3-3 Image-Recognition AI 3-4 CPU for Automated AI GPU, NPU, SoC 3-5 Memory for in-vehicle AI |
SDV Network
The SDV network configuration for Phase 3 would be as follows.
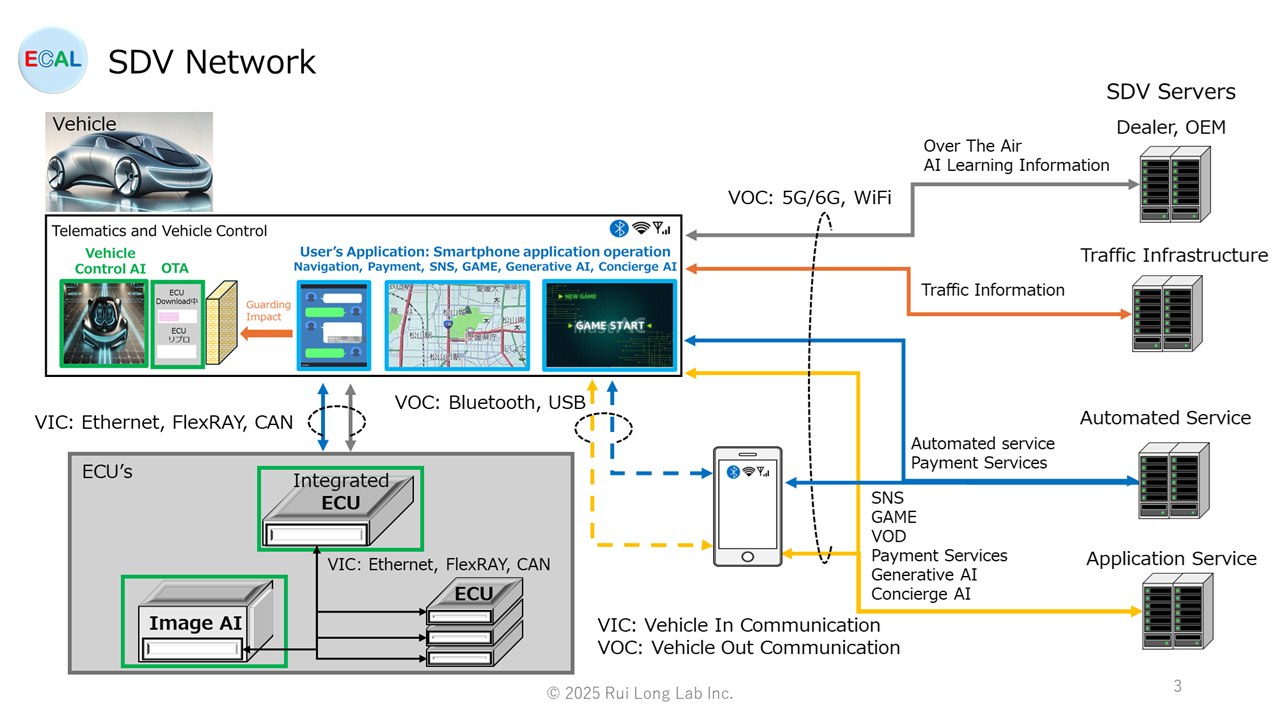
Communication Pprotocol
| SDV Servers | Telematics | VOC | 5G/6G, Wifi |
| Smartphone, Tablet PC | Telematics | VOC | Bluetooth, USB |
| Telematics | Integrated ECU, ECU’s | VIC | Ethernet, FlexRAY, CAN |
| Integrated ECU | ECU | VIC | Ethernet, FlexRAY, CAN |
| Integrated ECU | Image AI(ADAS) | VIC | Ethernet |
| ECU | ECU | VIC | FlexRAY, CAN |
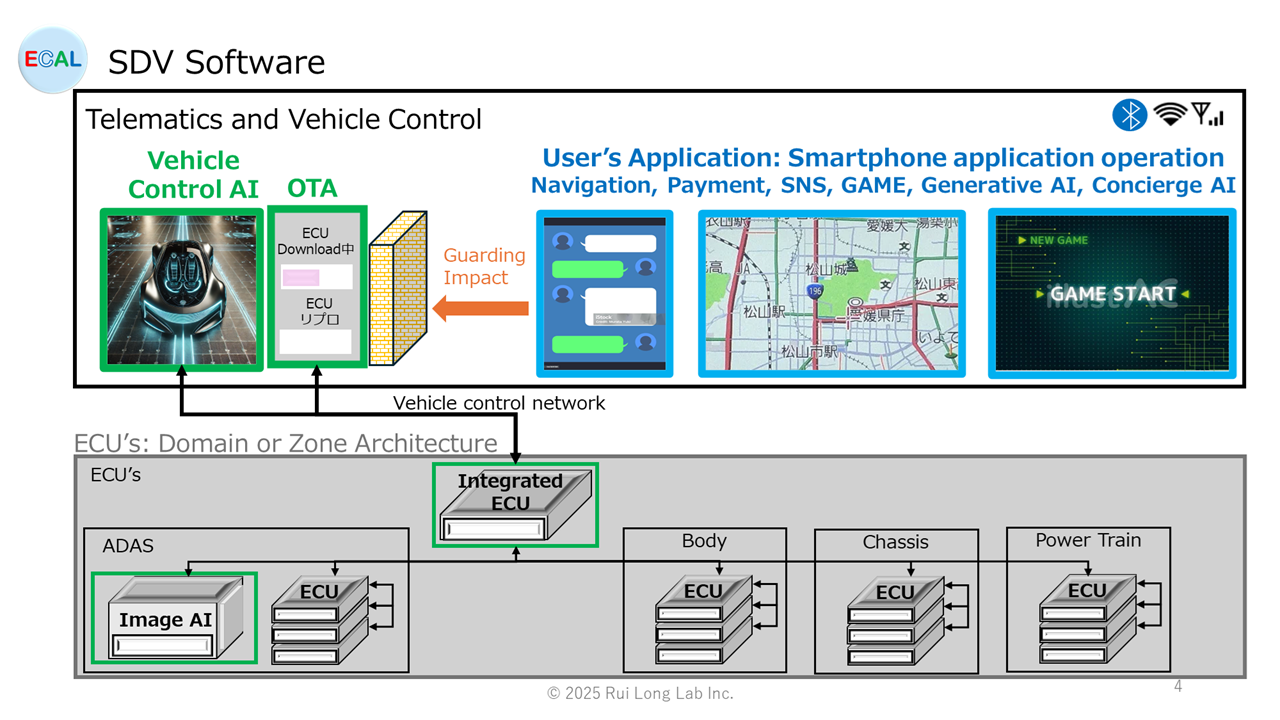
SDV Software
The in-vehicle software subject to SDV in Phase 3 would be as follows.
The important thing here is that functional safety must be ensured.Any malfunction in these software packages can cause serious accidents.For example, even smart phone applications are designed so that individual defects do not affect phone functionality.
- It is important to separate the Telematics User’s Application so that it does not affect the vehicle control and ECU application software.
- Just because updates can be made through OTAs does not mean that quality verification of vehicle control and ECU software should be released without due consideration.
| SDV software | In-vehicle equipment: Software | Software Developer and Provider | OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| OTA (Security included) | Telematics: OTA | OEM, Tire1 | Linux, AAOS**, iOS |
| Integrated ECU | OEM, Tire1 | Linux, RTOS | |
| ECU | OEM, Tire1 | Each ECU RTOS | |
| ADAS ECU | OEM, Tire1 | RTOS, SoC | |
| User’s Application | Telematics: User’s Application | Application provider | AAOS**, iOS |
| Telematics: User’s Application(Private Information Security) | OEM, Tire1 | AAOS**, iOS | |
| AI Learning Information (Security included) | Telematics: Vehicle Control AI* | OEM, Tire1, AI Service | Linux, SoC |
| Integrated ECU | OEM, Tire1 | Linux, RTOS | |
| Image AI* | OEM, Tire1, AI Service | Linux, SoC | |
| Traffic Information and Automated service (Security included) | Telematics: Navigation | Navi Service, Automated Service | AAOS**, iOS |
| VICS Center | AAOS**, iOS | ||
| Telematics: Vehicle Control AI* | OEM, Tire1, AI Service | Linux, SoC |
* In-vehicle AI requires high-performance CPUs (GPUs, NPUs, SoCs) and fast memory, developed by OEMs, Tier 1 and Tier 2
** AAOS: Android Automotive OS
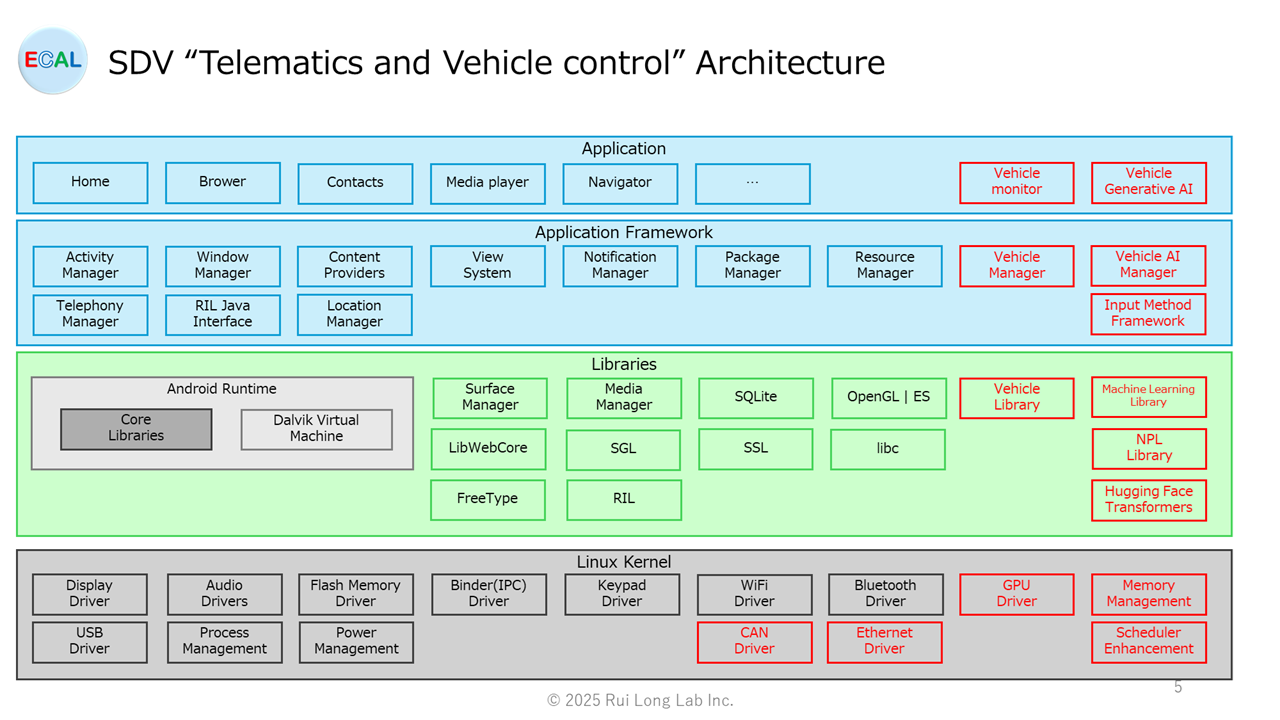
”Telematics and Vehicle control” architecture
The architecture of “Telematics and Vehicle control” was created with reference to AAOS.The parts in red are my own images, as I am not a specialist and have not studied enough.
OSS-ECAL adapts to the SDV era
SDV allows for many changes in ECU architecture; OSS-ECAL is an OSS with highly portable software components for sensors, actuators, and external memory.
ECU System
The ECU (Electronic Control Unit) domain architecture is summarized in the table below for ECUs.In the future, it will change to edge architecture, zone architecture, and edge & zone architecture according to the characteristics of each system.
| System | Unit Name | System Role |
|---|---|---|
| Powertrain system | ECU (Engine Control Unit) | Control of engine fuel injection, ignition, idle, etc. |
| ICU (Inverter Control Uint) | Control of EV/HEV motor drive (inverter/converter) | |
| TCU (Transmission Control Unit) | Control of AT/CVT/DCT gear shifting, etc. | |
| BMS (Battery Management System) | Management of EV/HEV battery level and temperature | |
| EMS (Energy Management System) | Control of energy optimization of the entire vehicle | |
| Chassis system | VCU (Vehicle Control Unit) | Integrated control of driving modes and vehicle behavior |
| EPS (Electric Power Steering System) | Steering wheel rudder angle control | |
| ESC (Electronic Stability Control) | Brake control to prevent slipping and rollover | |
| ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) | Brake control to prevent tire lock | |
| ECS (Electronic Controlled Suspension) | Suspension stiffness control | |
| AWD (All-Wheel Drive) | Control of driving force distribution for 4WD vehicles | |
| Body system | BCM (Body Control Module) | Control of lights, power windows, door locks, etc. |
| KOS (Keyless Operation System) | Keyless entry control, Engine start control | |
| HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) | Control of temperature and air volume adjustment of air conditioners and heaters | |
| LCU (Lamp Control Unit) | Control of headlights, taillights, and indicators | |
| SCU (Seat Control Unit) | Electric seat positioning and heater control | |
| RCU (Roof Control Unit) | Sunroof and convertible roof opening/closing control | |
| ADAS system | ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System) | Integrated control of collision avoidance, lane keeping, ACC, etc. |
| LKA (Lane Keep Assist) | Lane departure prevention and steering correction control | |
| AEB (Autonomous Emergency Braking) | Automatic braking control for collision avoidance | |
| ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control) | Control of maintaining distance from the vehicle ahead | |
| APA (Automatic Parking Assist) | Automatic parking assist control | |
| AVM (Around View Monitor) | Combines multiple camera images to display the vehicle’s surroundings |
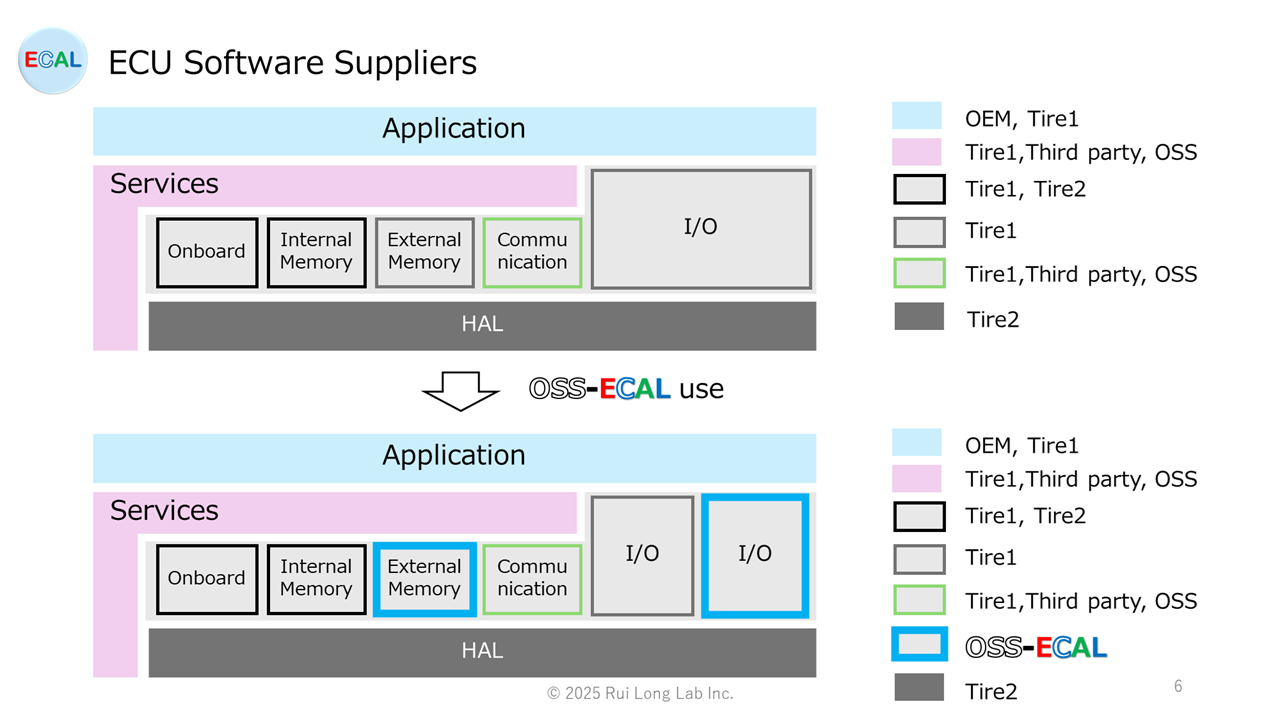
Domain architecture ECU software suppliers
The ECU software supplier in the Domain architecture would look like the figure below; the I/O and External EEPROM provided by Tire1 can be used with OSS-ECAL to improve efficiency.
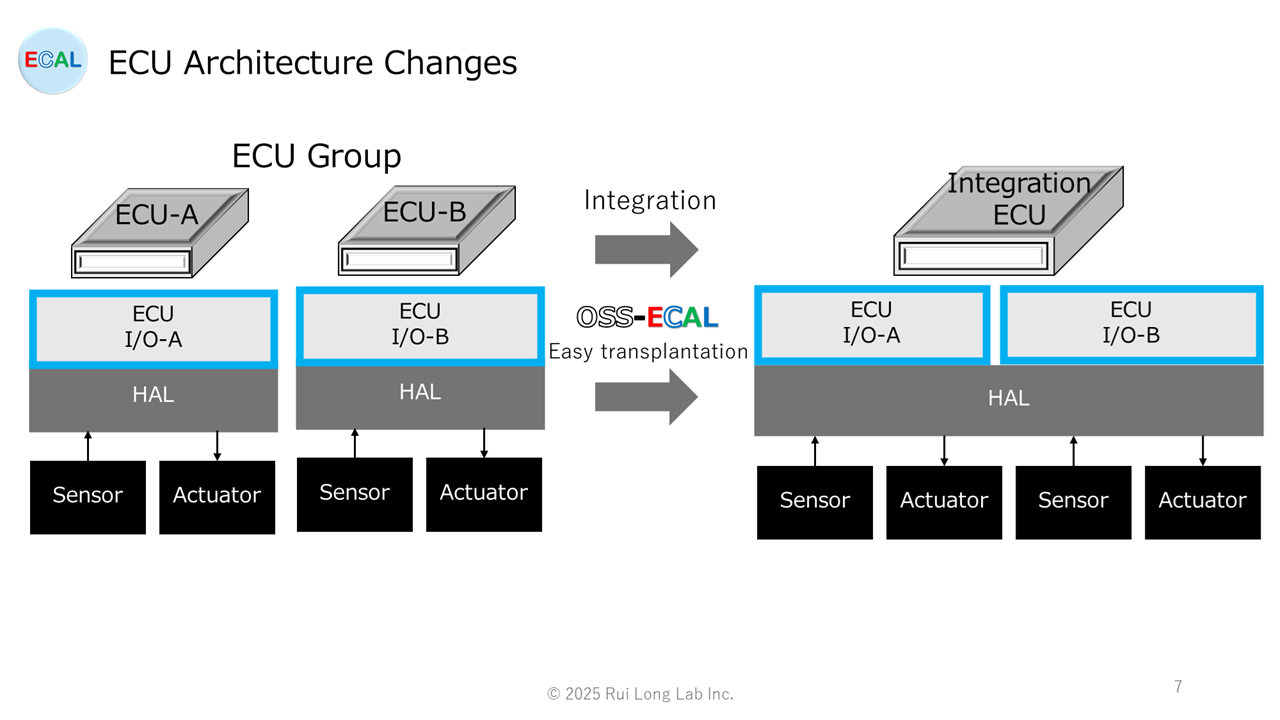
Moving sensors and actuators
Basically, sensors, actuators, external memory, etc. only change the ECU in which they are placed, whether in a domain architecture, edge architecture, zone architecture, or edge & zone architecture.Therefore, it is important that the software components of sensors, actuators, and external memory be highly portable, and OSS-ECAL is an OSS that emphasizes portability.
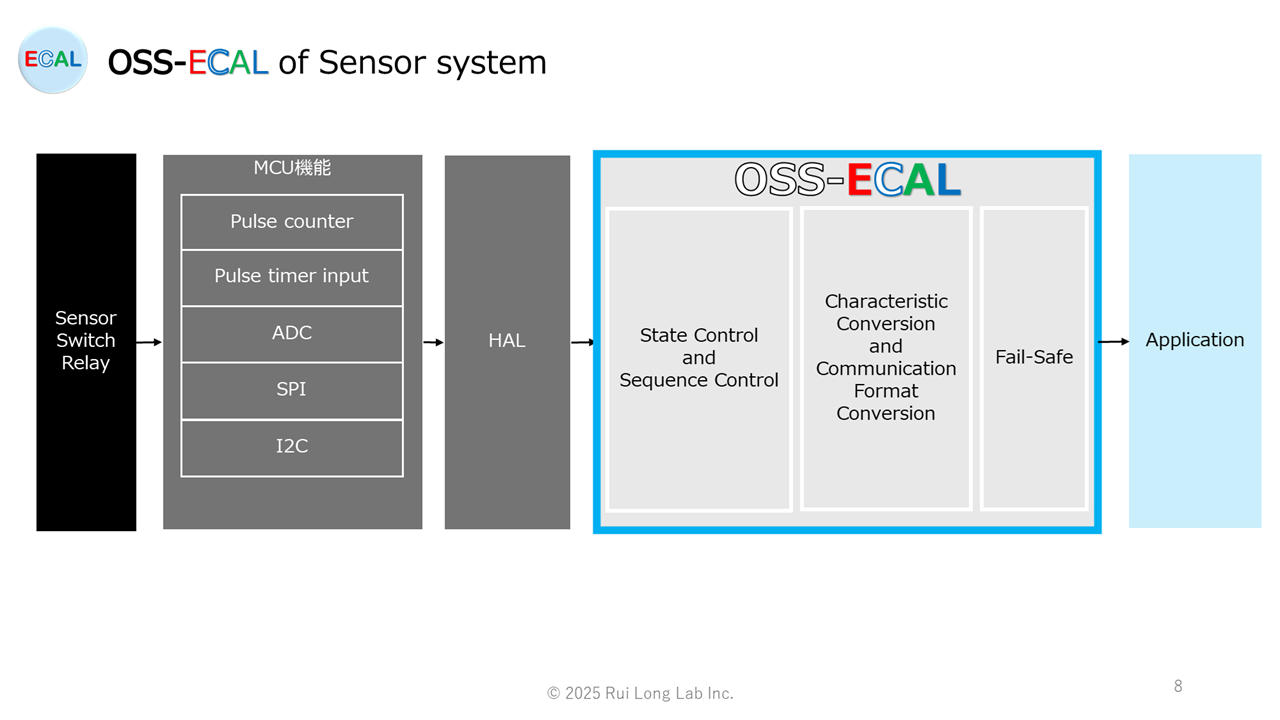
OSS-ECAL of Sensor system
The OSS-ECAL of sensor system is a software component with state transition and sequence control of sensor functions, communication format conversion, physical value conversion, HAL interface, fail-safe function, and sensor standard API. This ensures high portability and maintainability, and reliability through common application to various products.
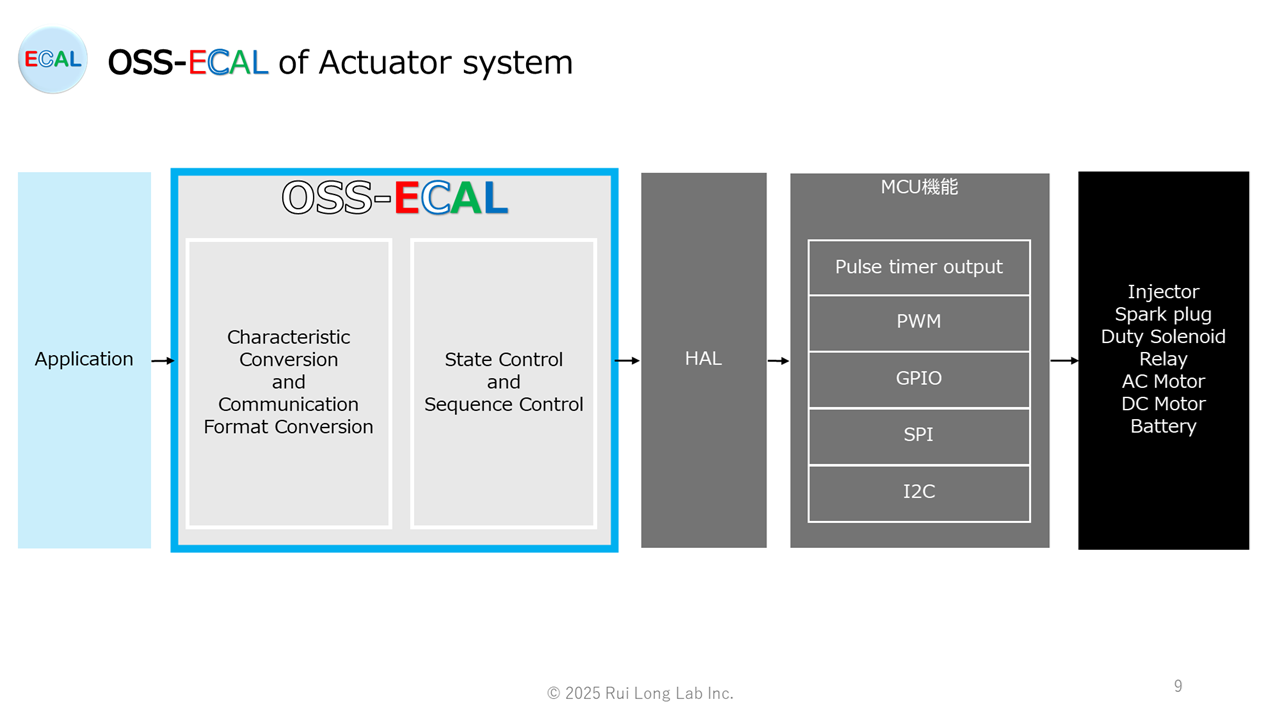
OSS-ECAL of Actuator system
The OSS-ECAL of actuator system is a software component with state transition and sequence control of actuator functions, communication format conversion, physical value conversion, HAL interface, fail-safe function, and actuators standard API. This ensures high portability and maintainability, and reliability through common application to various products.
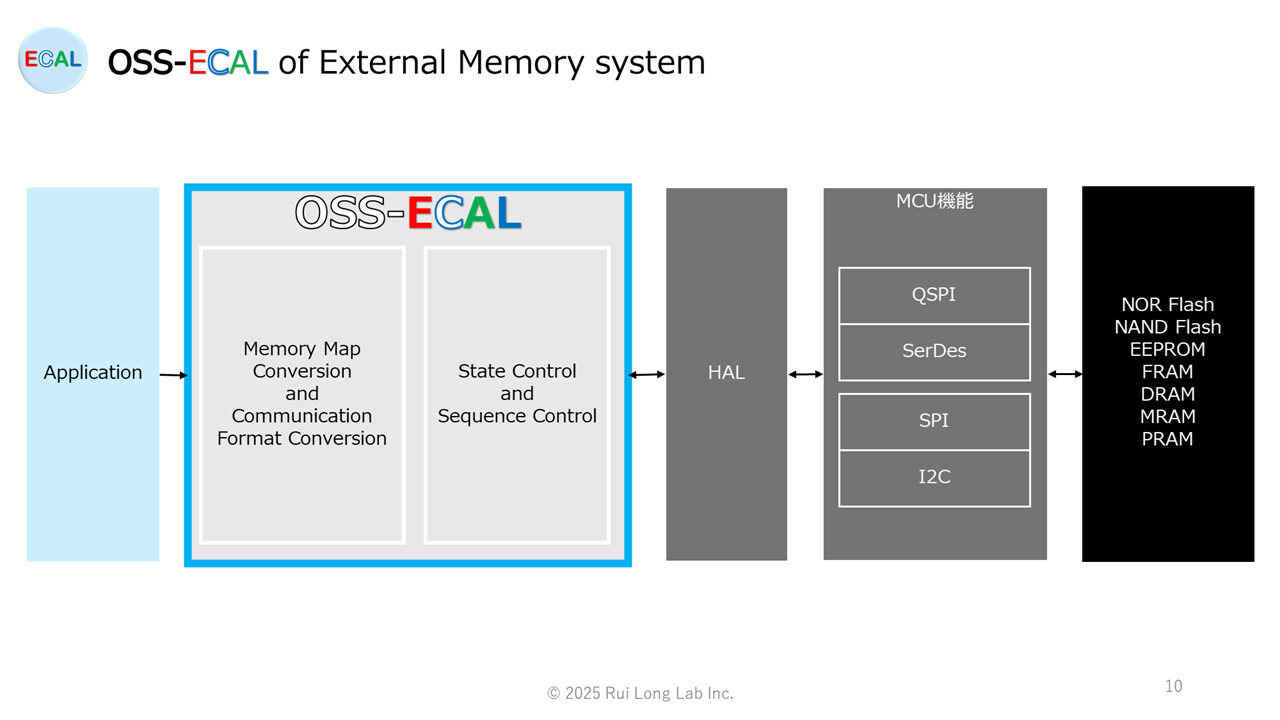
OSS-ECAL of External Memory system
The external memory system OSS-ECAL is a software component with state transition and sequence control of external memory functions, communication format conversion, HAL interface, fail-safe function, and external memory standard API. This ensures high portability and maintainability, and reliability through common application to various products.
Standardized APIs for electronic components
The OSS-ECAL API is aware of the part model number.However, the API can be standardized with #define.
Example: Application registration for temperature sensor ABC1
/* Temperature ABC1 read function*/
etSTS oABC1_READ( float32* );
#define TEMPERATURE_READ oABC1_READ
etSTS TEMPERATURE_READ( float32* rlt )Where to change the application when changing temperature sensor ABC1 to temperature sensor ABC2.The OSS-ECAL file should be replaced with the ABC2 file.
/* Temperature ABC2 read function*/
etSTS oABC2_READ( float32* );
#define TEMPERATURE_READ oABC2_READ
etSTS TEMPERATURE_READ( float32* rlt )Future OSS-ECAL for in-vehicle support
From now on, OSS-ECAL, our in-vehicle counterpart, would like to contribute to the development of the automotive industry by taking the following actions.
- Expansion of Automotive Electronic Components.
- OSS-ECAL add-on development for each MCU SDK tool.
- OSS-ECAL add-on development for Eclipse SDV and other SDV tools.
- Slimulink model development for OSS-ECAL
OEMs and Tire1 are requested to contact electronic component manufacturers or electronic component trading companies for any OSS-ECALs they require.
