This post describes DMA (Direct Memory Access).
DMA is a function that allows data transfer between MCU functions (communication, AD conversion, etc.) and RAM without involving the CPU.
Advantages
- CPU load reduction
- High-speed data transfer
- Deletion of interrupt processing
- Automation of sending and receiving
Disadvantages
- Bus occupied by DMA
- Complexity of DMA configuration
- DMA is difficult to detect failures
- DMA writes to RAM without passing through the cache, which may cause inconsistencies with the cache
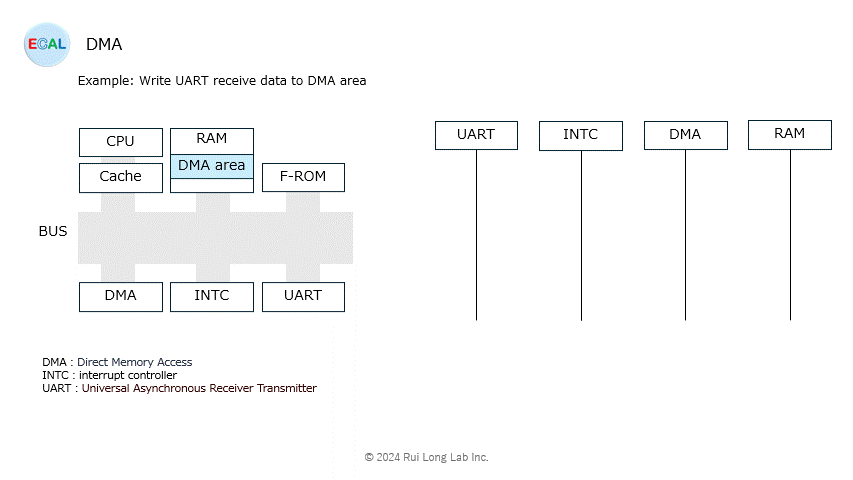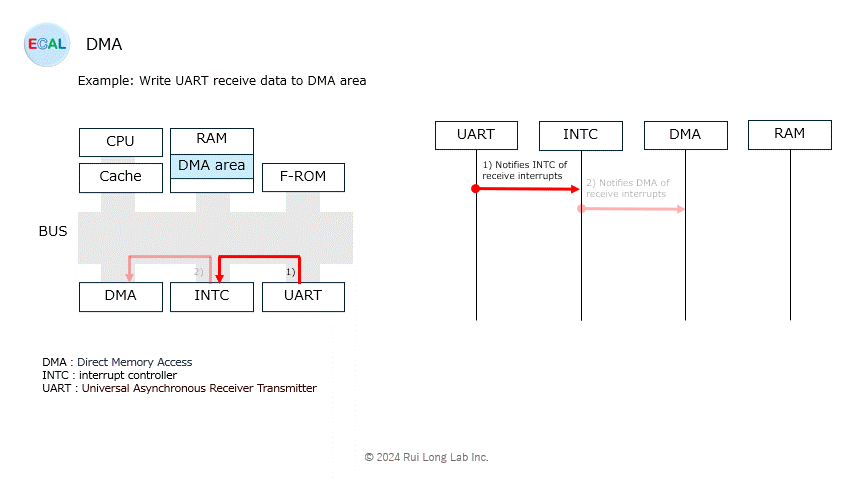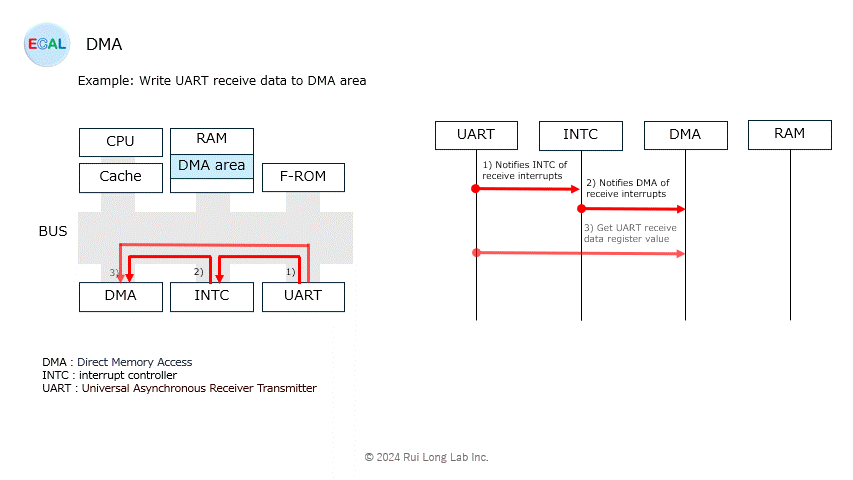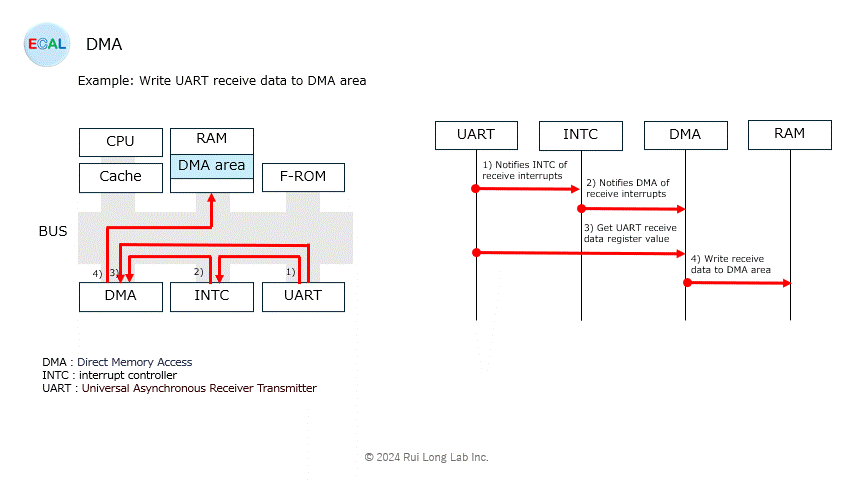
Arbitration (sharing of bus rights with the CPU) will be explained at another time.
