This post describes the CPU.
CPU
The CPU consists of CPU register and ALU (Arithmetic and Logic UNIT), Decoder UNIT, and Fetch UNIT.
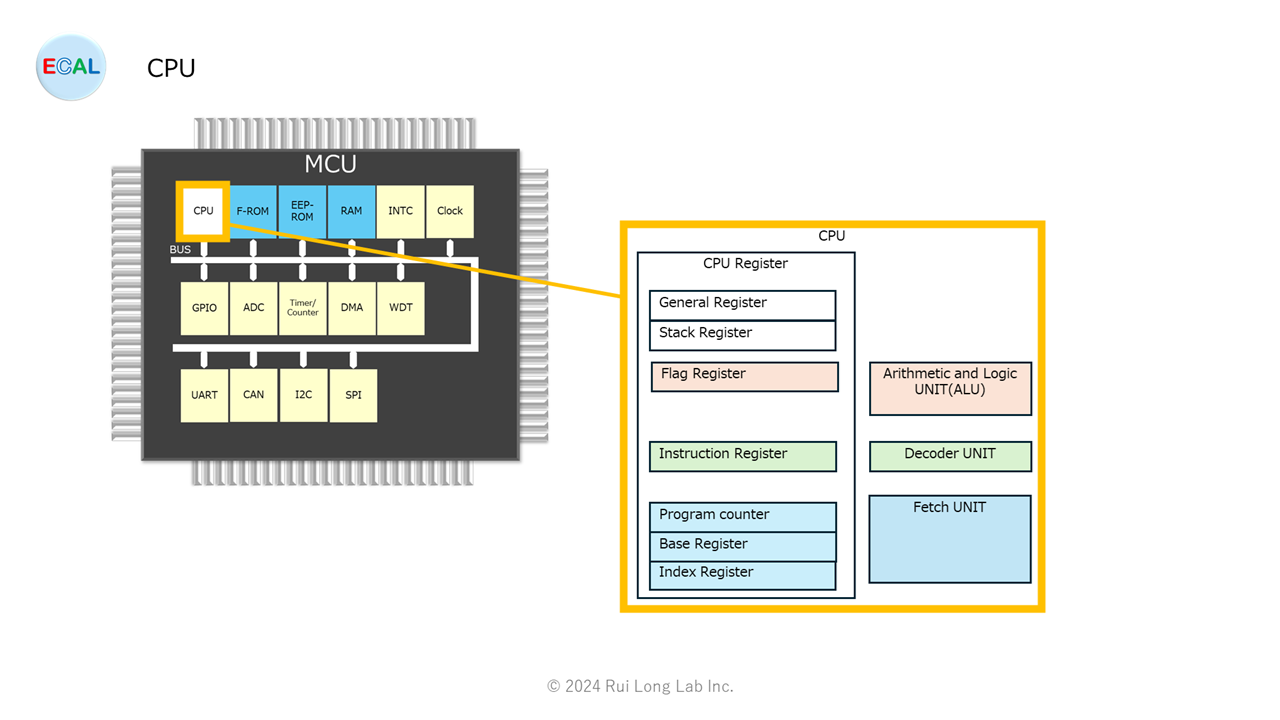
CPU registers
CPU registers consist of the General Register, Stack Register, Flag Register, Instruction Register, Program Counter, Base Register, and Index Register.
General Register
General Register is a register that can be used for general purposes.
Stack Register
Stack Register is a register that stores the top address of the stack pointer.
Flag Register
Flag Register is a register that stores whether the result of an operation performed by the ALU is a positive or negative value, or whether an overflow or underflow has occurred.
Instruction Register
Instruction Register is a register that stores instruction codes when instruction codes are fetched.
Program Counter
Program Counter is a register that stores the address value where the instruction code to be executed next is stored.
Base Register
Base Register is a register that stores the top address of the storage area to be accessed.
Index Register
Index Register is a register that stores the address relative to the address of the storage area to be accessed with respect to the base register.
ALU
The ALU consists of arithmetic circuits such as adders and logic operators, and performs the basic four arithmetic operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as logical operations such as OR (logical OR), AND (logical AND), and NOR (exclusive OR).
Decoder UNIT
The Decoder UNIT decodes instruction codes read from memory and controls registers, ALUs, and memory.
Fetch UNIT
The Fetch UNIT recalls instruction codes from addresses stored in the Program Counter and stores (fetches) them in the Instruction Register.
CPU execution cycle
The CPU execution cycle repeats Fetch, Decode, and Execute.

Fetch
Fetch reads an instruction code from the memory address of the instruction code stored in the Program counter and stores the read instruction code in the Instruction Register. The Program counter increments to the next instruction code address.
Decode
The decode step involves decode- ing the instruction code stored in the instruction register, calculating the execution address of the data that is the target of the instruction code, and storing the data from that execution address in a general-purpose register.
Executing an instruction
Executing an instruction means executing the instruction code. For example, if the instruction code is a calculation, the values stored in the general registers during decoding are calculated by the ALU, and the results are stored in the general registers.
