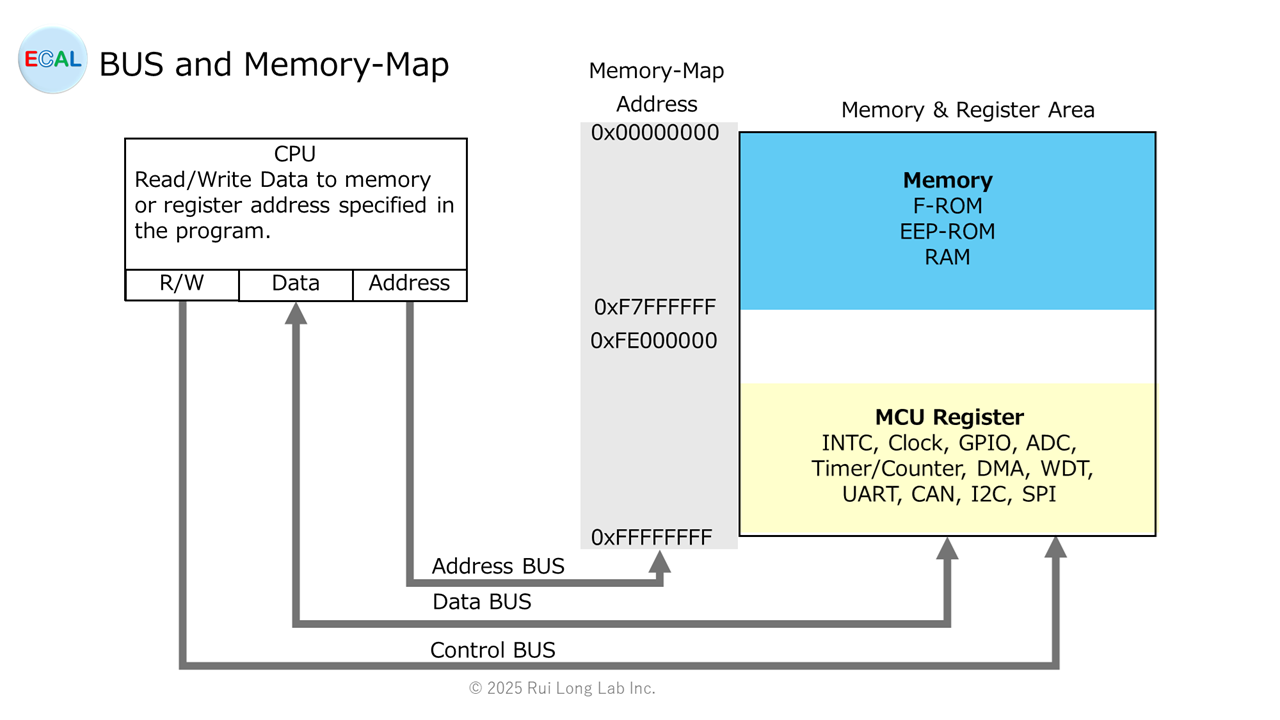
This post describes the BUS and Memory-map.
The BUS is a transmission path that connects the CPU with internal control units (Clock, INTC), memory units (RAM, F-ROM, EEP-ROM), external signal input/output units (GPIO, ADC), communication units (UART, CAN, I2C, SPI), and internal and external control units (Timer/Counter, DMA).
The Address BUS is the transmission path for the addresses of the memory and UNIT Rregisters of each unit as specified by the CPU. The width of the transmission path can be 8, 16, or 32 bits long, depending on the MCU.
The Data BUS is the transmission path for data in the memory and UNIT Rregisters of each unit as specified by the CPU. The width of the transmission path can be 8, 16, or 32 bits long, depending on the MCU. The transmission direction changes depending on the Read/Write of the Control BUS.
The Control BUS is a signal line that controls data Read/Write.
The memory map maps the addresses of each unit’s memory and UNIT Registers.