This post introduces the characteristics and differences of the V-process for each phase of an embedded product. Please note that this may vary greatly from product to product.
The development phase of embedded products can be broadly divided into the prototype development phase and the mass production development phase, as shown below.
Prototype Development Phase
Purpose
Prototype development is intended to confirm and verify the design or concept of a new product or an improvement of a conventional product.
Features
– Confirmation and verification of designs and concepts can be performed in MBD during the initial design phase.
– Create a small number of prototypes and confirm and verify them with actual products.
– Respond quickly to processes such as agile development.
Mass Production Development Phase
Purpose
Mass production development is aimed at mass production of products and focuses on ensuring cost efficiency and quality stability. Based on the products established in prototype development, it may also be expanded according to product grade and other factors. For example, in the case of automobiles, development is carried out according to the car model, grade, and destination.
Features
– Focus on dates.
– Focus on quality.
– Cost optimization.
– Manufacturing Optimization.
– Delivery Optimization.
– Product Deployment.
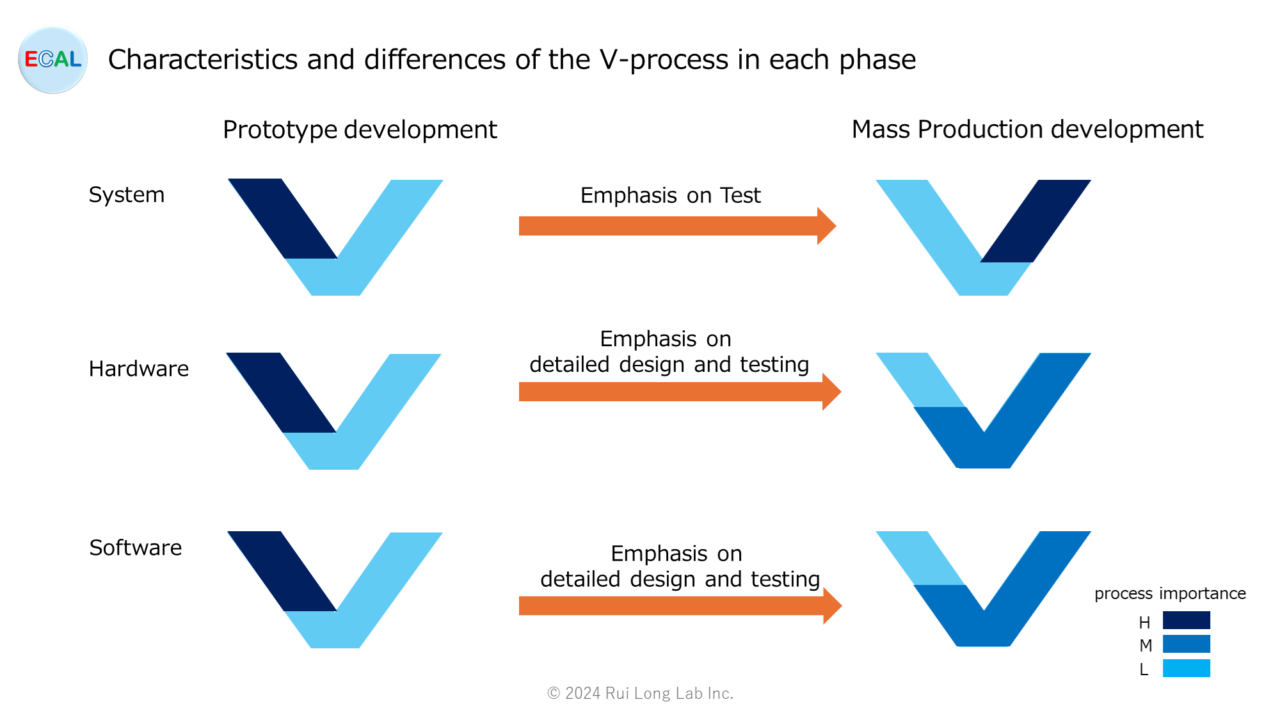
Characteristics and differences of the V-process in each phase
As shown in the table below, each phase has different important requirements and processes to focus on. However, many quality standards are defined without reflecting these realities, and as a result, many companies do not flexibly change their quality manuals and design rules according to the phases, which in some cases deviates from the actual situation. Please note that this may result in work to be done later or affect product planning.
Please note that unexpected problems may arise if the impact scope test process is not defined.
Table . Critical Requirements and Critical Processes for Each Process by Phase
| Phase | System | HW | SW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prototype Development | Key requirements – Function*, performance – Housing, weight – Mass production cost Key processes – Requirement elicitation – System requirements analysis – Architecture design – MBD, MILS | Key requirements – Function*, performance – Housing, weight – Mass production cost – Productivity Key processes – Hardware requirements analysis – HW architecture design – Circuit design – Circuit simulation – Pattern design – Selection of materials, components, and parts – Prototype test environment construction | Key requirements – Function*, performance – Encapsulation – Development efficiency Key processes – Basic design RTOS setting MCU function setting Peripheral IC setting File structure Memory allocation Shared resource access method – State transition design – SW architecture design |
| Mass Production Development | Key requirements – Function*, performance – Quality standards compliance Key processes – MBD, MILS – System integration and integration testing – System qualification test – System impact scope test | Key requirements – Function*, performance – Quality standards compliance – Reliability – Productivity, yield – Environ mentality – Delivery – Mass production cost Key processes – Selection and procurement of parts – Design of reliability tests – Building of manufacturing line – Building of test environment for mass-produced products – HW impact scope test | Key requirements – Function*, performance – Quality standards compliance – Project management – Reliability Key processes – SW detailed design – SW unit testing – SW integration and integration testing – SW impact scope test |
* Functions include functional safety